With the capability to capture and analyze data from devices in isolated areas, SCADA systems have a unique place in the technological advancement of the 21st century. Entering the 2017-2022 period, the need for integrated and scalable solutions stretches beyond the highly-industrialized economies to developing countries. Thus, smart technologies that help optimize costs become a necessity, especially in highly competitive industries such as utilities.
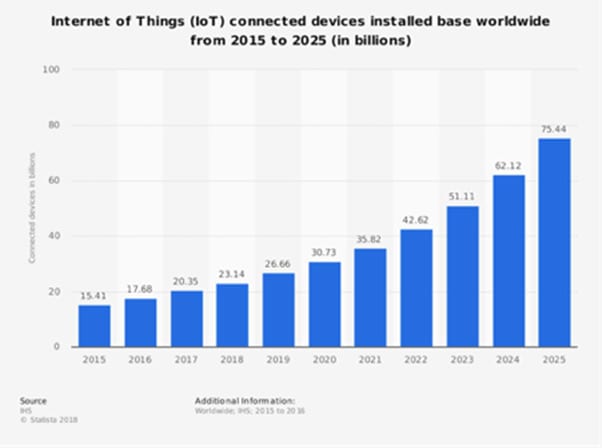
Thanks to their scalability and ease of updating and upgrading, electrical SCADA are amongst the leaders in market expansion. They are estimated to expand at a CAGR (Compound Annual Growth Rate) of 7.8%, reaching $3.29 billion by 2022. Urban infrastructure (electricity grid, traffic control and water supply included) already relies heavily on SCADA for its day-to-day and long-term maintenance. Some segments, however, are expected to outpace others in the aforementioned period.
Distribution Segment
Experts stipulate that the distribution segment will lead the way with the highest CAGR for the period 2017-2022. This is a new occurrence as up to this point the hardware segment was the leader in the adoption of SCADA technology.
The need for automation development is the main powerhouse supporting the rapid new technology adoption. As energy, used throughout the distribution chain, never reaches the end customer, improvements are due in order for companies to remain competitively active. SCADA systems can provide the much needed data and automation to cut down energy losses.
Hardware Segment
The hardware segment has previously championed the SCADA market and is deemed to remain at the top at least until 2022. As before, the hardware segment is the main enabler of technological progress for the utility companies around the globe. This factor alone is predicted to continue driving sales in the long-term.
Geographical Distribution of SCADA
A peculiar trend arises in the developing countries where companies prefer to directly adopt SCADA systems rather than going through the lengthy and costly technological steps that precede modern SCADA. With the playfield less than even for developed and developing countries, geographical and political factors influence the adoption rate of electrical SCADA.
Here are the most significant geopolitical factors that predetermine the high CAGR:
- Mexican government has agreed to grid monetization that will involve serious SCADA implementation.
- European utilities are also vigorously upgrading or directly replacing their SCADA systems to improve scalability and better meet the new demands of the ever evolving digital grid, supported by sustainability directives.
- USA and Canada have traditions in keeping pace with new technologies and will continue updating the SCADA technology they already have in place.
- Asia-Pacific is expected to become the fastest growing market for SCADA with China and India paving the way. A stellar example of their progressive undertaking are the 100 Smart Cities Mission, announced by the Government of India.
Impacting Factors
Infrastructure
With the planning and development of smart cities, sustainable public transportation and innovative electrical grid, global and local infrastructure will drive the demand for smart SCADA solutions to new heights.
Compliance Requirements
Modern SCADA systems are integrated with not only with computers but also with mobile devices. This increased mobility is a highly sought-after factor in the system’s usability.
Big Data Analytics
One of SCADA’s main USPs (unique selling propositions) is yet again exploited for the electric industry. Analytical solutions are vital for reducing errors, identifying root-causes of critical problems and, last but not least, improving and speeding up decision-making.