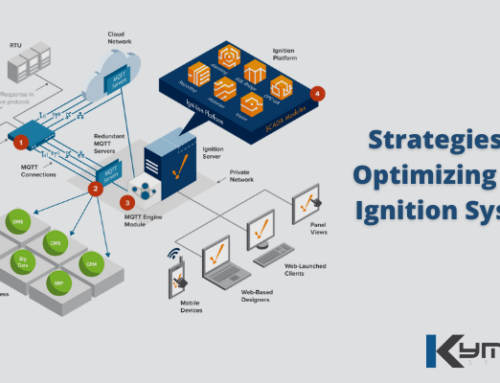
The Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) is rapidly transforming the way manufacturing and other industries are conducting their business. These innovative technologies brought forth by IIoT allow companies to collect and share data in more precise and flexible ways. They can combine both data analytics and M2M communication, as well as data acquisition software to transform any business into a much faster and smarter enterprise.
Today’s industrial sector is driven by a wide series of devices that control and safeguard both property and personnel. In more recent years, however, older machinery has been updated or replaced by newer models. These are fitted with all sorts of smart sensors – running mostly on wireless networks. This way, they provide a more streamlined operation that can cut on costs, reduce the risk of accidents, and increase overall productivity. Nevertheless, this interconnectivity has also increased the risk of a security breach.
A hacker could remotely take over a facility and input commands that can cause all sorts of problems such as the disruption of certain processes, violation of protocols, dangerous or even catastrophic safety overrides, and much more. All of these can result in both property damages, lost revenue, or much worse. If a cyber-attack were to take place on an oil rig, nuclear power plant, or a city’s water treatment facility, the consequences could be dire.
Education
As both informational technology (IT) and operational technology (OT) are coming together, facility operators and other qualified personnel need to know the risks that are involved when it comes to such factors like cyber-attacks. There are many areas moving at any given time, and the biggest challenge in matters of cybersecurity is knowing where to begin.
The first step in understanding this threat is to bring both IT and OT personnel together to build trust, increase inter-department communications, and work on ways to develop and implement technologies that can safeguard against these kinds of threats.
The next step is to determine what software, machinery, or protocols can be vulnerable to such attacks. Various industrial controllers need to be given special attention. These include batch control systems, production control servers, automated systems, OPC (Open Platform Communications) systems, SCADA systems, cameras, and other peripheral devices.
Intrusion prevention software is a critical element in safeguarding the facility. These are tuned to operate over a multitude of endpoints within the facility. This software needs to be able to understand all of the industrial protocols that involve programmable logic controllers (PLCs), as well as human-machine interfaces (HMI). It should be able to detect any anomalies such as the atypical movement of a robotic arm or a sudden change in temperature, for instance.
Conclusion
The implementation of IIoT technology is a welcomed addition to the industrial world, as it can enhance productivity, reduce risk and liability, and increase productivity. Nevertheless, safeguarding against cyber-attacks is an absolute must. Certain software vulnerabilities such as Meltdown and Spectre have proven the need and importance of security in this digital world.